Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Epidemiol Health > Volume 40; 2018 > Article
-
Original Article
Effects of human and organizational deficiencies on workers’ safety behavior at a mining site in Iran -
Mostafa Mirzaei Aliabadi1
 , Hamed Aghaei2
, Hamed Aghaei2 , Omid Kalatpour1
, Omid Kalatpour1 , Ali Reza Soltanian3
, Ali Reza Soltanian3 , Maryam SeyedTabib3
, Maryam SeyedTabib3
-
Epidemiol Health 2018;40:e2018019.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2018019
Published online: May 18, 2018
1Center of Excellence for Occupational Health Engineering, Occupational Health and Safety Research Center, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
2Center of Excellence for Occupational Health Engineering, School of Public Health and Research Center for Health Sciences, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
3Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health and Modeling of Non-Communicable Diseases Research Center, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
- Correspondence: Hamed Aghaei Center of Excellence for Occupational Health Engineering, School of Public Health and Research Center for Health Sciences, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, P.O. Box 6517838695, Hamadan, Iran E-mail: h.aghaei@umsha.ac.ir
©2018, Korean Society of Epidemiology
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
OBJECTIVES
- Throughout the world, mines are dangerous workplaces with high accident rates. According to the Statistical Center of Iran, the number of occupational accidents in Iranian mines has increased in recent years. This study investigated and analyzed the human and organizational deficiencies that influenced Iranian mining accidents.
-
METHODS
- In this study, the data associated with 305 mining accidents were analyzed using a systems analysis approach to identify critical deficiencies in organizational influences, unsafe supervision, preconditions for unsafe acts, and workers’ unsafe acts. Partial least square structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) was utilized to model the interactions among these deficiencies.
-
RESULTS
- Organizational deficiencies had a direct positive effect on workers’ violations (path coefficient, 0.16) and workers’ errors (path coefficient, 0.23). The effect of unsafe supervision on workers’ violations and workers’ errors was also significant, with path coefficients of 0.14 and 0.20, respectively. Likewise, preconditions for unsafe acts had a significant effect on both workers’ violations (path coefficient, 0.16) and workers’ errors (path coefficient, 0.21). Moreover, organizational deficiencies had an indirect positive effect on workers’ unsafe acts, mediated by unsafe supervision and preconditions for unsafe acts. Among the variables examined in the current study, organizational influences had the strongest impact on workers’ unsafe acts.
-
CONCLUSIONS
- Organizational deficiencies were found to be the main cause of accidents in the mining sector, as they affected all other aspects of system safety. In order to prevent occupational accidents, organizational deficiencies should be modified first.
- The mining industry plays a crucial role in the economy of countries throughout the world. Despite extensive efforts to improve safety in mines, accidents remain a threat to the sustainability of the mining industry, as they can lead to injuries and death among workers, property degradation, and damage to the environment [1]. According to previous studies, the rate of accidents in the mining industry is very considerable [2].
- Several studies have investigated the main causes of accidents in the mining industry. A study of mining accidents in the US attributed nearly 85% of mine accidents to human error [1]. Since human behavior in a complex socio-technical system such as the mining industry is affected by various organizational and environmental factors, it cannot be correct to consider human error to be the main cause of accidents [3]. Some studies have reported that inappropriate working conditions, such as rock falls and explosions, were the main causes of mining accidents [4,5]. A number of studies have identified inadequacies in management measures, such as a lack of proper training courses for workers and inadequate supervision, as the main causes of mining accidents [4,6,7]. However, a comprehensive analysis for identifying the causal factors of accidents has not been conducted yet. Determining the interactions between causal factors of accidents can lead to better comprehension of the defects in the system. System-based accident analysis models can help to understand why accidents occur, and identifying patterns of accidents would be helpful for preventing their reoccurrence [2].
- Multiple system-based accident analysis models have been developed [8,9]. The human factors analysis and classification system (HFACS) is one of the most widely used and reliable accident analysis models [10], and was developed by Wiegmann & Shappell [3] based on the Swiss cheese model [9]. Instead of introducing humans as the main cause of accidents, the HFACS systematically seeks to recognize the active and latent errors in the system that can eventually result in an accident. The HFACS model categorizes 19 causal factors in a hierarchical order of 4 levels of human and organizational failures, including unsafe acts, preconditions for unsafe acts, unsafe supervision, and organizational influences. In this approach, investigators first identify the types of unsafe acts that are thought to lead to the accident, and then look for the root causes of the accident at the organizational and supervisory levels. Based on the HFACS approach, at least 1 deficiency is present at each level when an accident occurs. If the organization corrects any of the failures that results in an accident, the accident will be avoided.
- The HFACS was first introduced to analyze aviation accidents [3], and then has been employed in other areas such as marine accidents [11,12], clinical errors [13,14], and rail incidents [15,16]. Some studies have utilized the HFACS for analyzing mining accidents. Patterson & Shappell [17] applied a modified version of the HFACS to analyze 508 mining accidents with the goal of recognizing the human and organizational deficiencies that led to mining accidents in Queensland. In another study, Lenné et al. [18] used the original HFACS to characterize the relationships of organizational and supervisory failures with unsafe acts of the operator in mining accidents. Verma & Chaudhari [19] analyzed human factors contributing to Indian manganese mining accidents using a modified version of the HFACS. However, no studies have conducted a comprehensive analysis to determine the relationships and interactions among the human and organizational deficiencies that contribute to mining accidents.
- According to the Statistical Center of Iran, Iran had 5,316 active mines in 2012, from which more than 60 minerals were extracted. Iran is among the top 15 mineral-rich countries, and more than 100,000 people are employed in the mining industry directly and approximately 2 million more people indirectly. Unfortunately, the number of occupational accidents in Iranian mines has increased from 876 cases in 2009 to 1,177 cases in 2012 [20,21]; however, a large number of work-related accidents may has not been reported by organizations. Thus, the present study focused on analyzing Iranian mining accidents based on the HFACS model to identify human and organizational deficiencies and to determine the interactions between these deficiencies by using partial least square structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM).
- Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a powerful analysis tool from the multivariable regression family that allows a set of regression equations to be tested simultaneously. SEM is a comprehensive statistical approach for testing hypotheses about relationships between observed and latent variables [22,23]. Covariancebased structural equation modeling (CB-SEM) and PLS-SEM are the 2 main approaches for estimating SEM [24]. In the CB-SEM approach, the proposed model is examined using a covariance matrix, while in the PLS-SEM approach, the model is assessed by describing the variance in the variables. PLS-SEM is recommended when the data do not follow a multivariate normal distribution, few data are available, and the model is formative [25].
INTRODUCTION
- Data source and coding process
- Reports of 305 significant mining accidents involving considerable property damage, fatality, or serious injuries occurring between 2002 and 2016 and results of the accident analysis were gathered from one of the largest iron ore mines in Kerman, Iran. The company employed an accident analysis team with various experts to analyze significant accidents. Accident analysis was performed using the root cause analysis (RCA) approach. RCA is a problem-solving approach utilized to identify the root causes of problems [26].
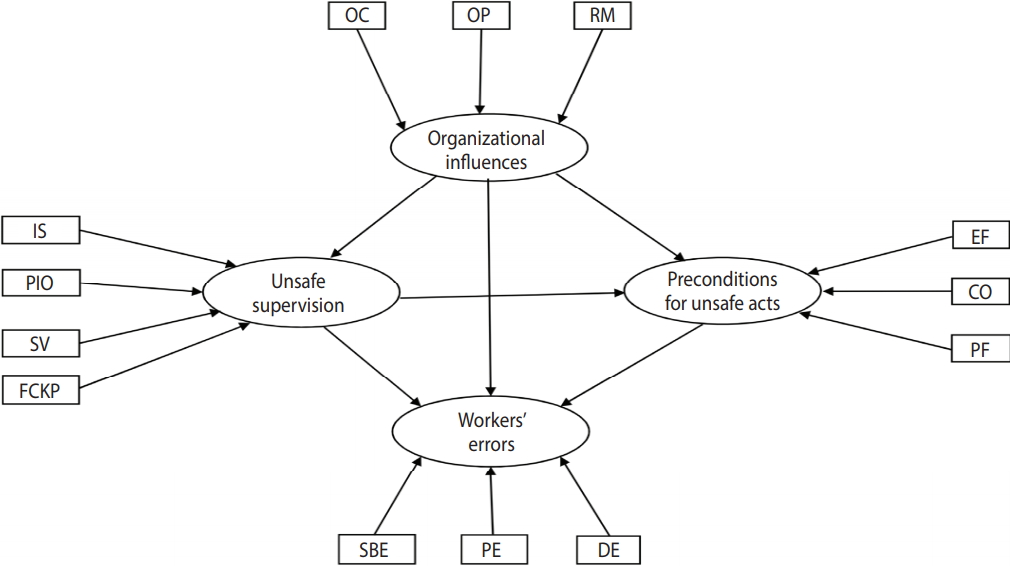
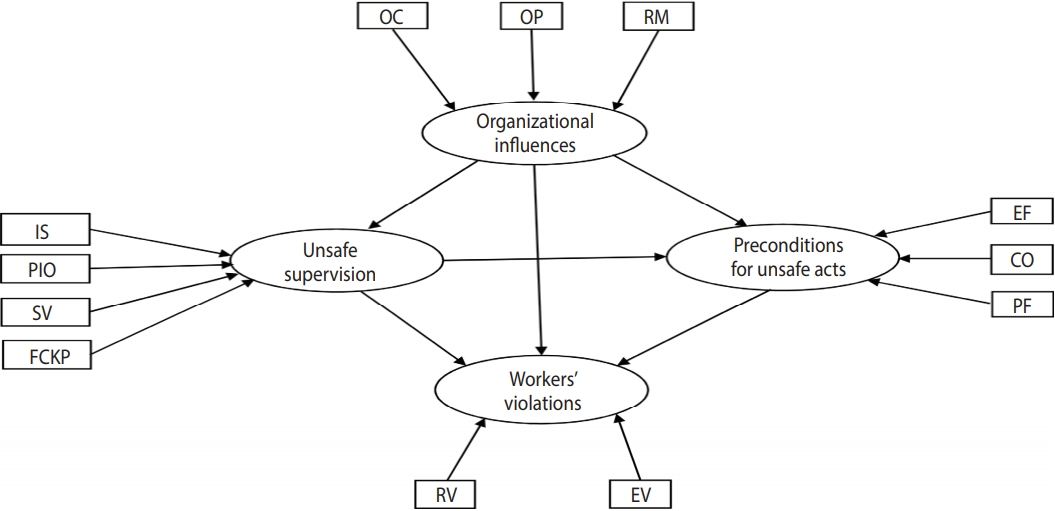
- As mentioned earlier, the HFACS has 4 levels. Level 1 is workers’ unsafe acts and includes 2 categories: workers’ errors and workers’ violations. An error is an unintentional action of a worker that can result in an accident, while a violation is an intentional disregard of rules and regulations that can also result in an accident [3]. Violation should not be conflated with sabotage, because the former category includes actions that generally have the goal of completing tasks faster and in a more effective manner, while the latter category refers to actions carried out with the aim of damaging the system. Level 2 contains the preconditions for unsafe acts, including various physical and technological factors, adverse mental/physiological states, and physical limitations of workers that can contribute to an unsafe act or accident. Preconditions for unsafe acts include environmental factors, condition of operator, and personnel factors [3]. Level 3 corresponds to unsafe supervision, which refers to supervisors’ disregard of safety problems in the workplace. Unsafe supervision is subdivided into 4 subcategories: inadequate supervision, planned inappropriate operation, failed to correct known problem, and supervisory violations [3]. Level 4 refers to organizational influences, or deficiencies at the top management level that affect the likelihood of an accident. Organizational influences are subdivided into 3 subcategories: resource management, organizational climate, and operational process [3].
- In the present study, workers’ unsafe acts, preconditions for unsafe acts, unsafe supervision, and organizational influences were regarded as latent variables, and categories related to each variable that could be determined directly were regarded as their indicators. The latent variables and their related indicators are presented in Table 1.
- Each indicator was regarded as a binary variable, for which a score of 0 meant that the indicator did not contribute to the accident, and a score of 1 meant that the indicator contributed to the accident. To determine the score of each indicator in each accident (the coding process), 2 ergonomists with 4 years of experience in the mining industry were asked to assign a score to the variables based on accident data, such as accident report forms, photographs of the accident, and RCA results. All accidents were coded based on the above-described procedure and a database was created. The coding process was performed by consensus to increase inter-rater reliability.
- Building the model
- SEM models are normally constructed based on the hypotheses that are to be examined. Since a previous study [1] demonstrated that 85% of mining accidents occurred due to workers’ unsafe acts, in the present study, the influence of system deficiencies on workers’ unsafe acts was evaluated based on the following hypotheses:
- Hypothesis 1: Organizational influences exert a direct impact on unsafe acts of workers; Hypothesis 2: The effect of organizational influences on unsafe acts of workers is mediated by unsafe supervision; Hypothesis 3: The effect of organizational influences on unsafe acts of workers is mediated by preconditions for unsafe acts; Hypothesis 4: Organizational influences have an impact on unsafe acts of workers through a sequence of unsafe supervision and preconditions for unsafe acts.
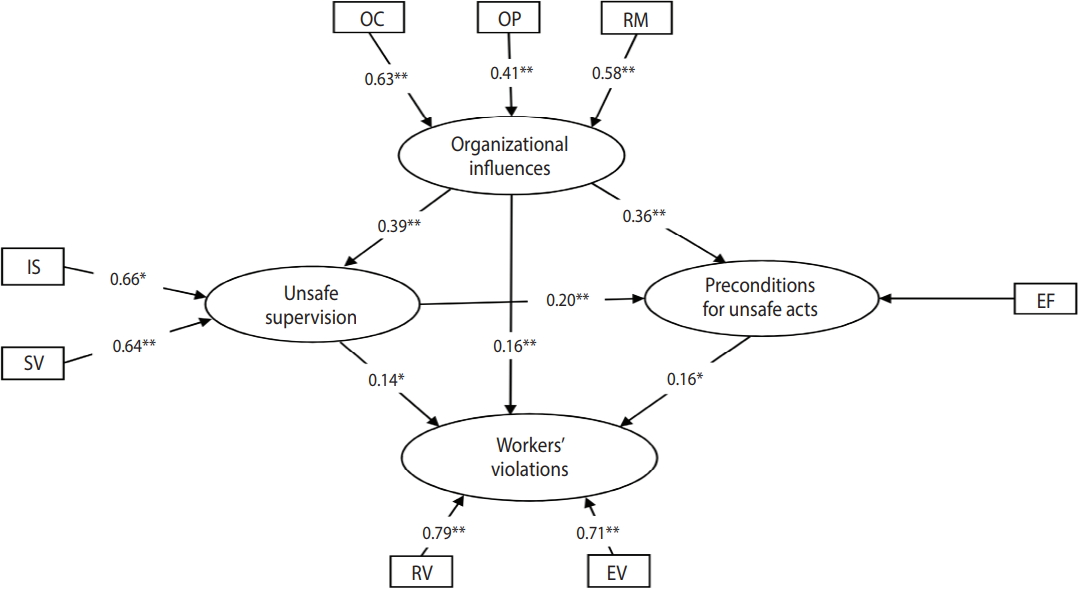
- Since workers’ unsafe acts can be divided into errors and violations, we examined the above hypotheses for workers’ violations and for workers’ errors separately. The proposed models are illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 for workers’ violations and workers’ errors, respectively.
- The database was imported into SmartPLS 2.0 (https://www.smartpls.com/smartpls2) and the hypotheses of the present study were examined using the bootstrap method. Since the applied model in this study was formative and few data were available, PLSSEM was employed [25]. Following Zhang et al. [27], the process of data analysis with PLS-SEM for verifying the theoretical model was performed in 2 steps. In the first step, the quality of the measurement model (individual indicator validity) was evaluated. Various indices were used to assess the measurement model according to the type of the indicators in the model [28]. Since the proposed models in the present study had formative indicators, we used the indicator weight to determine which indicators should be eliminated and which should be retained in the model [28]. Accordingly, after running PLS-SEM, the significant indicators and the non-significant ones weighted more than 0.5 were retained in the model, while the others were excluded.
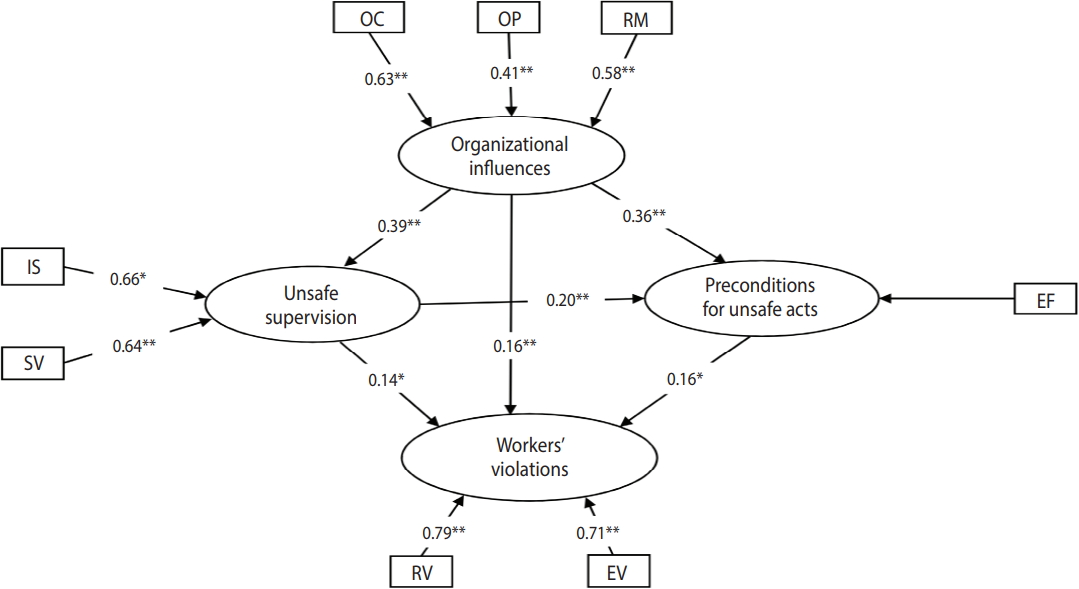
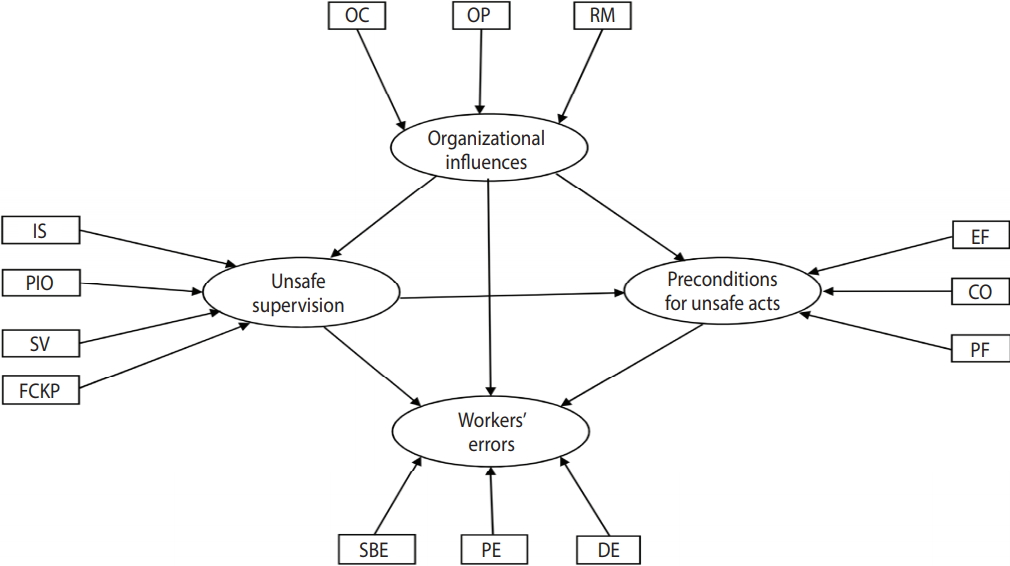
- After determining the indicators that needed to be retained in the 2 models, the data were analyzed again, and new indicator weights and t-values were calculated (Figures 3 and 4). As shown in Figures 3 and 4, all indicators in the 2 models were significant (p< 0.05). After evaluating the quality of the measurement model, the second step was to evaluate the structural model (construct validity). In this step, using R2 , cross-validated redundancy (CV-Red), cross-validated communality (CV-Com), and goodness-of-fit (GoF) indices that were fitted to the model with formative indicators [25,28], the quality of the structural model was evaluated. R2 is a measure of the variance explained in each of the endogenous latent variables. CV-Com assesses how much each latent variable is useful to the model adjustment and CV-Red assesses the accuracy of the adjusted model. GoF assesses the quality of the adjusted model [25]. Table 2 show the results of structural evaluation of the models of workers’ violations and workers’ errors, respectively.
- As Table 2 shows, CV-Red and CV-Com were acceptable for all latent variables in the model of workers’ violations. Additionally, R2 values were 15.48, 23.25, and 13.50%, respectively, for unsafe supervision, preconditions for unsafe acts, and workers’ violations. Table 2 shows that CV-Red and CV-Com were acceptable for all latent variables in the model of workers’ errors. Unsafe supervision (R2 , 18.10%), preconditions for unsafe acts (R2 , 22.32%), and workers’ errors (R2 , 13.22%) had a medium effect on workers’ errors. We determined the GoF for the workers’ violations and workers’ errors models to be 0.32 and 0.28, respectively, which indicated that the 2 models had an adequate adjustment [29].
- The study protocol was approved by the Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (ethical code: IR.UMSHA.REC.1395.458).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- A total of 305 mining accidents were investigated. All the workers involved in the accidents were men, with a mean age of 33.0±7.6 years and an average experience of 7.6± 4.3 years. Moreover, 76% of them were married and the rest were single.
- Before interpreting the results of PLS-SEM, the quality of the proposed models was assessed in 2 steps and the suitability of the proposed models was confirmed (Figures 3 and 4). Based on Figure 3, among the 3 indicators of the organizational influences variable, the organizational climate had the greatest effect (indicator weight, 0.63) and the organizational process had the least effect (indicator weight, 0.41). Inadequate supervision (indicator weight, 0.66) and supervisory violations (indicator weight, 0.64) had a nearly equal influence on the unsafe supervision variable. Since among all the indicators of the preconditions for unsafe acts variable, only environmental factors were retained in the workers’ violations model, this indicator had the greatest effect on preconditions for unsafe acts. Of the 2 indicators of the workers’ violations variable, routine violations had a greater effect than exceptional violations.
- In the workers’ errors model (Figure 4), resource management had the most influence on the organizational influences, while organizational process had the least. Planned inappropriate operation and inadequate supervision had a large effect on unsafe supervision, whereas supervisory violations had a small effect. Furthermore, environmental factors were the indicator with the greatest effect on the preconditions for unsafe acts. Among the 3 indicators of the workers’ errors variable, skill-based errors had the greatest effect and perceptual errors had the least effect.
- Hypotheses 1 to 4 aimed at assessing the interactions among unsafe acts of workers and organizational influences, unsafe supervision, and preconditions for unsafe acts. As shown in Figure 3, workers’ violations were positively affected by the organizational influences (path coefficient, 0.16) and this effect was statistically significant (p< 0.01). Therefore, hypothesis 1 was confirmed for the workers’ violations model. Moreover, the impact of organizational influences on workers’ violations was mediated by unsafe supervision because the path from organizational influences to unsafe supervision and the path from unsafe supervision to workers’ violations were statistically significant; hence, hypothesis 2 was supported. Additionally, as shown in Figure 3, the impact of organizational influences on workers’ violations was mediated by preconditions for unsafe acts (environmental factors), thereby confirming hypothesis 3. Furthermore, organizational influences impacted workers’ violations through a sequence of unsafe supervision and preconditions for unsafe acts; therefore, hypothesis 4 was confirmed (Figure 3).
- Figure 4 shows the interactions among latent variables in the model of workers’ errors. Organizational influences had a direct positive effect (path coefficient, 0.23) on workers’ errors, and this effect was statistically significant (p< 0.05), confirming hypothesis 1. Organizational influences had a significant effect on unsafe supervision (p< 0.01) and unsafe supervision had a statistically significant effect on workers’ errors (p< 0.05), thereby supporting hypothesis 2. Hypothesis 3 was confirmed, because the impact of organizational influences on preconditions for unsafe acts was statistically significant, as was the impact on preconditions for unsafe acts on workers’ errors. Finally, organizational influences impacted errors through the sequence of unsafe supervision and preconditions for unsafe acts to a statistically significant extent; therefore, hypothesis 4 was also supported.
RESULTS
- Workers’ unsafe acts are usually considered to be the main cause of industrial accidents. However, in complex systems, humans are only one of multiple mutually-interacting system components. In the analysis of unsafe acts, these interactions should be taken into account. Therefore, several studies have suggested that accidents should be investigated and analyzed using systematic methods to recognize deficiencies in all components of the system [32,33]. A comprehensive investigation of accidents using systematic analysis methods can help to gain a deep understanding of the relationships and interactions among system components [34]. In the present study, mining accidents were analyzed using the HFACS as a reliable system-based method, and interactions between human and organizational factors were examined with PLS-SEM.
- In the present study, based on the PLS-SEM results, hypotheses 1 to 4 for the models of workers’ unsafe acts were supported. According to hypothesis 1, organizational deficiencies have a direct effect on workers’ unsafe acts. Some studies [27,35] demonstrated that organizational factors such as deficiencies in safety management, organizational involvement, and unsafe rules directly affected workers’ unsafe acts. Moreover, other studies [36,37] showed that safety culture and work pressure were organizational factors that affected workers’ unsafe acts. Time pressure and a high workload can affect human error and the efficiency of operators [38].
- Hypothesis 2 states that organizational deficiencies exert an effect on workers’ unsafe acts mediated by unsafe supervision. According to the psychosocial model of workplace accidents, the organizational safety climate influences workers’ safety behavior, mediated by supervisors’ safety responses [39]. Therefore, the role of supervisors as a mediator between management rules/policies and workers can have a crucial effect on workers’ safe acts. Indeed, supervisors can provide a supportive environment for safety in which safety behavior is encouraged. Several studies have explained that one of the main reasons why workers do not engage in safe behavior is the fear of being teased by coworkers [40]. Another reason is that some workers regard safety behavior as a sign of weakness [41]. Both these examples are indicative of a workplace with a poor supportive environment. However, it should be noted that the lack of a supportive environment is a sign of poor management commitment to safety. In other words, when safety is important for managers, it is important for supervisors too, thus resulting in a supportive environment for safety behavior [42]. Indeed, management commitment to safety is crucial for providing a supportive environment for safety. Moreover, when supervisors ignore safety rules and regulations, frontline employees may lose their motivation to engage in safe behavior; in such a situation, reward and punishment systems are also meaningless and the effectiveness of incentive systems cannot be maintained in the long term [43].
- In this study, hypothesis 3 was also confirmed, meaning that managerial lack of attention towards solving environmental and technological problems, such as lack of funding for the necessary technological tools for the workplace, can lead to workers’ unsafe acts. For this reason, mines are harsh and polluted workplaces. In such a poor working environment, workers are uncomfortable and tend to take shortcuts when performing their tasks, consequently ignoring safety issues and increasing the risk of accidents. This pattern has also been observed among outdoor workers. Several studies have found the rate of unsafe behavior to increase during the middle of the day when the outdoor temperature is at its peak [44]. Likewise, the finding is in accordance with the results obtained by Ramsey et al. [45], who found that the rate of safety behavior decreased as the thermal conditions of the workplace deviated from the optimum range. In the same vein, the effect of environmental factors on safety behavior has also been investigated by some other studies [46]. Therefore, more attention from management to housekeeping, ventilation systems, and thermal comfort may be helpful as a way to decrease accidents by improving environmental factors.
- Finally, hypothesis 4 was supported, indicating that organizational influences affect unsafe acts of workers through a sequence of unsafe supervision and preconditions for unsafe acts. In fact, organizational factors such as management commitment to safety are essential for improving health and safety issues in workplaces. Without management commitment, safety programs are unlikely to succeed [47]. Inadequate staffing is another organization-related factor that can affect safety behavior and accidents [48]. When the number of workers in the workplace is lower than what is needed, workers must work fast, perform several tasks simultaneously, and take shortcuts. Consequently, their attention decreases and the probability of error increases. Moreover, this result is in agreement with the study by Lenné et al. [18] that analyzed major mining accidents based on the HFACS model and found that there was a significant relationship among certain contributing factors in the organization, supervision, preconditions for unsafe acts, and workers’ unsafe act levels. System-based accident analysis models suggest that the elimination of latent errors across a sophisticated system is the most appropriate strategy for preventing accidents, instead of addressing the active errors of workers. This is also in accordance with the conceptual model proposed by Neal et al. [49], which argues that organizational climate is the root cause of poor safety performance.
- Some strengths and limitations of this study should be acknowledged. In the present study, many mining accidents were investigated, meaning that the sample size was a major strong point of the study. Another strong point was the use of a systematic and well-accepted framework as a basis for the PLS-SEM model. However, this study also had some limitations that should be mentioned. A major limitation is that the accident data investigated in the present study were obtained from a single mining site in Iran; hence, it is recommended for future studies to consider more accidents from various mining sites. Moreover, although PLS-SEM is a powerful method for interaction analysis, other methods, such as Bayesian networks [50], are recommended for developing predictive models.
- In conclusion, organizational deficiencies were found to be the main causes of mining accidents. These deficiencies have both direct and indirect effects on unsafe acts. Organizational deficiencies can also lead to unsafe supervision and preconditions for unsafe acts. Without modifying these deficiencies, attempts to prevent mining accidents would probably fail to achieve the desired results. Therefore, in order to reduce the rate of mining accidents, deficiencies at higher organizational levels should be addressed.
DISCUSSION
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS

| Latent variable | R2 (%)1 | CV-Red | CV-Com |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workers’ violations | |||
| Organizational influences | - | 0.38 | 0.38 |
| Unsafe supervision | 15.48 | 0.09 | 0.67 |
| Preconditions for unsafe acts | 23.25 | 0.24 | 0.99 |
| Workers’ violations | 13.50 | 0.07 | 0.42 |
| Workers’ errors | |||
| Organizational influences | - | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| Unsafe supervision | 18.10 | 0.09 | 0.42 |
| Preconditions for unsafe acts | 22.32 | 0.23 | 0.99 |
| Workers’ errors | 13.22 | 0.08 | 0.30 |
| Criteria | 2.00, 13.00, and 26.00: small, medium, and large effect, respectively [30] | 0<CV-Red [31] |
- 1. Bonsu J, van Dyk W, Franzidis JP, Petersen F, Isafiade A. A systemic study of mining accident causality: an analysis of 91 mining accidents from a platinum mine in South Africa. J South Afr Inst Min Metall 2017;117:59-66.Article
- 2. Bonsu J, van Dyk W, Franzidis JP, Petersen F, Isafiade A. A systems approach to mining safety: an application of the Swiss cheese model. J South Afr Inst Min Metall 2016;116:776-784.Article
- 3. Wiegmann DA, Shappell SA. A human error approach to aviation accident analysis: the human factors analysis and classification system; 2003 [cited 2018 Jun 29]. Available from: https://dvikan.no/ntnu-studentserver/reports/A%20Human%20Error%20 Approach%20to%20Aviation%20Accident%20Analysis.pdf.Article
- 4. Sanmiquel L, Freijo M, Edo J, Rossell JM. Analysis of work related accidents in the Spanish mining sector from 1982-2006. J Safety Res 2010;41:1-7.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Martín JE, Rivas T, Matías JM, Taboada J, Argüelles A. A Bayesian network analysis of workplace accidents caused by falls from a height. Saf Sci 2009;47:206-214.Article
- 6. Zhang M, Kecojevic V, Komljenovic D. Investigation of haul truckrelated fatal accidents in surface mining using fault tree analysis. Saf Sci 2014;65:106-117.Article
- 7. Ural S, Demirkol S. Evaluation of occupational safety and health in surface mines. Saf Sci 2008;46:1016-1024.Article
- 8. Leveson N. A new accident model for engineering safer systems. Saf Sci 2004;42:237-270.Article
- 9. Reason J. Human error. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1990. p 173-216.
- 10. Salmon PM, Cornelissen M, Trotter MJ. Systems-based accident analysis methods: a comparison of Accimap, HFACS, and STAMP. Saf Sci 2012;50:1158-1170.Article
- 11. Chen ST, Wall A, Davies P, Yang Z, Wang J, Chou YH. A Human and Organisational Factors (HOFs) analysis method for marine casualties using HFACS-Maritime Accidents (HFACS-MA). Saf Sci 2013;60:105-114.Article
- 12. Wang YF, Xie M, Chin KS, Fu XJ. Accident analysis model based on Bayesian Network and Evidential Reasoning approach. J Loss Prev Process Ind 2013;26:10-21.Article
- 13. Mitchell RJ, Williamson A, Molesworth B. Application of a human factors classification framework for patient safety to identify precursor and contributing factors to adverse clinical incidents in hospital. Appl Ergon 2016;52:185-195.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Diller T, Helmrich G, Dunning S. Cox S, Buchanan A, Shappell S. The human factors analysis classification system (HFACS) applied to health care. Am J Med Qual 2014;29:181-190.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Zhan Q, Zheng W, Zhao B. A hybrid human and organizational analysis method for railway accidents based on HFACS-Railway Accidents (HFACS-RAs). Saf Sci 2017;91:232-250.Article
- 16. Reinach S, Viale A. Application of a human error framework to conduct train accident/incident investigations. Accid Anal Prev 2006;38:396-406.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Patterson JM, Shappell SA. Operator error and system deficiencies: analysis of 508 mining incidents and accidents from Queensland, Australia using HFACS. Accid Anal Prev 2010;42:1379-1385.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Lenné MG, Salmon PM, Liu CC, Trotter M. A systems approach to accident causation in mining: an application of the HFACS method. Accid Anal Prev 2012;48:111-117.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Verma S, Chaudhari S. Safety of workers in Indian mines: study, analysis, and prediction. Saf Health Work 2017;8:267-275.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Bagherpour R, Yarahmadi R, Khademian A, Almasi SN. Safety survey of Iran’s mines and comparison to some other countries. Int J Inj Contr Saf Promot 2017;24:3-9.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Statistical Center of Iran. Survey results of Iran’s active mines in 2012 [cited 2018 Jul 10]. Available from: https://www.amar.org.ir/Portals/0/Files/fulltext/1395/naamdhbs94.pdf (Persian).
- 22. Chung JH, Lee D. Structural model of automobile demand in Korea. Transp Res Rec 2002;1807:87-91.Article
- 23. Golob TF. Structural equation modeling for travel behavior research. Transport Res B Meth 2003;37:1-25.Article
- 24. Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Smith D, Reams R, Hair JF. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): a useful tool for family business researchers. J Fam Bus Strategy 2014;5:105-115.Article
- 25. Hair JF, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Mena JA. An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J Acad Mark Sci 2012;40:414-433.Article
- 26. Wilson P, Dell L, Anderson G. Root cause analysis: a tool for total quality management. Milwaukee:: ASQC Quality Press; 1993. p 8-17.
- 27. Zhang Y, Shao W, Zhang M, Li H, Yin S, Xu Y. Analysis 320 coal mine accidents using structural equation modeling with unsafe conditions of the rules and regulations as exogenous variables. Accid Anal Prev 2016;92:189-201.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Sanchez G. PLS path modeling with R [cited 2018 Jun 29]. Available from: http://www.gastonsanchez.com/PLS_Path_Modeling_ with_R.pdf.
- 29. Wetzels M, Odekerken-Schröder G, van Oppen C. Using PLS path modeling for assessing hierarchical construct models: guide-lines and empirical illustration. MIS Q 2009;33:177-195.Article
- 30. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988. p 407-465.
- 31. Hair JF, Hult GTM, Ringle CM, Sarstedt MA. A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Los Angeles: Sage Publications; 2013. p 167-201.
- 32. Goh YM, Brown H, Spickett J. Applying systems thinking concepts in the analysis of major incidents and safety culture. Saf Sci 2010;48:302-309.Article
- 33. Dekker S, Cilliers P, Hofmeyr JH. The complexity of failure: implications of complexity theory for safety investigations. Saf Sci 2011;49:939-945.Article
- 34. Dekker SW, Nyce JM. Cognitive engineering and the moral theology and witchcraft of cause. Cogn Technol Work 2012;14:207 - 212.Article
- 35. Oliver A, Cheyne A, Tomás JM, Cox S. The effects of organizational and individual factors on occupational accidents. J Occup Organ Psychol 2002;75:473-488.Article
- 36. Brown KA, Willis PG, Prussia GE. Predicting safe employee behavior in the steel industry: development and test of a sociotechnical model. J Oper Manag 2000;18:445-465.Article
- 37. Ghasemi F, Kalatpour O, Moghimbeigi A, Mohhamadfam I. A path analysis model for explaining unsafe behavior in workplaces: the effect of perceived work pressure. Int J Occup Saf Ergon 2018;24:303-310.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Zarei E, Mohammadfam I, Aliabadi MM, Jamshidi A, Ghasemi F. Efficiency prediction of control room operators based on human reliability analysis and dynamic decision-making style in the process industry. Process Saf Prog 2016;35:192-199.Article
- 39. Fugas CS, Silva SA, Meliá JL. Another look at safety climate and safety behavior: deepening the cognitive and social mediator mechanisms. Accid Anal Prev 2012;45:468-477.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Mullen J. Investigating factors that influence individual safety behavior at work. J Safety Res 2004;35:275-285.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Choudhry RM, Fang D. Why operatives engage in unsafe work behavior: investigating factors on construction sites. Saf Sci 2008;46:566-584.Article
- 42. Mohammadfam I, Ghasemi F, Kalatpour O, Moghimbeigi A. Constructing a Bayesian network model for improving safety behavior of employees at workplaces. Appl Ergon 2017;58:35-47.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Ghasemi F, Mohammadfam I, Soltanian AR, Mahmoudi S, Zarei E. Surprising incentive: an instrument for promoting safety performance of construction employees. Saf Health Work 2015;6:227-232.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Ghasemi F, Kalatpour O, Moghimbeigi A, Mohammadfam I. Selecting strategies to reduce high-risk unsafe work behaviors using the safety behavior sampling technique and Bayesian network analysis. J Res Health Sci 2017;17:e00372.PubMed
- 45. Ramsey JD, Burford CL, Beshir MY, Jensen RC. Effects of workplace thermal conditions on safe work behavior. J Safety Res 1983;14:105-114.Article
- 46. Zhen-Dong LI. SEM-based study on effects of organizational and environmental factors on workers’ unsafe behavior. China Saf Sci J 2012;11:004.
- 47. Hopkins A. Making safety work: getting management commitment to occupational health and safety. St. Leonards: Allen and Unwin; 1995. p 117-123.
- 48. Strauch B. Can we examine safety culture in accident investigations, or should we? Saf Sci 2015;77:102-111.Article
- 49. Neal A, Griffin MA, Hart PM. The impact of organizational climate on safety climate and individual behavior. Saf Sci 2000;34:99-109.Article
- 50. Mirzaei Aliabadi M, Aghaei H, Kalatpour O, Soltanian AR, Nikravesh A. Analysis of human and organizational factors that influence mining accidents based on Bayesian network. Int J Occup Saf Ergon 2018;doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10803548.2018.1455411.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Exploring the application of PLS-SEM in construction management research: a bibliometric and meta-analysis approach
Sachin Batra
Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of characteristics and causes of gas explosion accidents: a historical review of coal mine accidents in China
Yunxin Wang, Gui Fu, Qian Lyu, Chenhui Yuan
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2024; 30(1): 168. CrossRef - A fuzzy Bayesian network DEMATEL model for predicting safety behavior
Mohsen Mahdinia, Iraj Mohammadfam, Ahmad Soltanzadeh, Mostafa Mirzaei Aliabadi, Hamed Aghaei
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2023; 29(1): 36. CrossRef - Assessing the impact of peripheral vision on construction site safety
Isik Ates Kiral, Sevilay Demirkesen
Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management.2023; 30(9): 4435. CrossRef - Modelling and analysis of unsafe acts in coal mine gas explosion accidents based on network theory
Wang Yuxin, Fu Gui, Lyu Qian, Li Xiao, Chen Yiran, Wu Yali, Xie Xuecai
Process Safety and Environmental Protection.2023; 170: 28. CrossRef - Conceptual Framework for Hazards Management in the Surface Mining Industry—Application of Structural Equation Modeling
Saira Sherin, Salim Raza, Ishaq Ahmad
Safety.2023; 9(2): 31. CrossRef - Identification and evaluation of maintenance error in catalyst replacement using the HEART technique under a fuzzy environment
Mostafa Mirzaei Aliabadi, Iraj Mohammadfam, Keyvan Salimi
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2022; 28(2): 1291. CrossRef - Influencing Factors, Formation Mechanism, and Pre-control Methods of Coal Miners′ Unsafe Behavior: A Systematic Literature Review
Li Yang, Xue Wang, Junqi Zhu, Zhiyuan Qin
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors Identification of Unsafe Acts in Deep Coal Mine Workers Based on Grounded Theory and HFACS
Li Yang, Xue Wang, Junqi Zhu, Zhiyuan Qin
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of AHP and DEMATEL for Identifying Factors Influencing Coal Mine Practitioners’ Unsafe State
Lei Chen, Hongxia Li, Shuicheng Tian
Sustainability.2022; 14(21): 14511. CrossRef - Integrated Method for Assessing Occupational Risks at Oil and Gas Production Facilities
N V Gorlenko, M A Murzin
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2021; 666(6): 062141. CrossRef - Integrated Method for Assessing Occupational Risks at Oil and Gas Production Facilities
N V Gorlenko, M A Murzin
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1079(6): 062078. CrossRef - Occupational Risk Assessment for Workers of Aluminum Production Using the Example of RUSAL Bratsk OJSC
M A Murzin, M S Tepina, N V Gorlenko
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1079(6): 062080. CrossRef - Zero-Emission Water Cycle When Developing Underground Gas Storage in Rock Salt Formation
E A Lokshina, A V Kolchin, B N Mastobaev
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1079(7): 072039. CrossRef - Research trends in mining accidents study: A systematic literature review
Siti Noraishah Ismail, Azizan Ramli, Hanida Abdul Aziz
Safety Science.2021; 143: 105438. CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship among Human Factors in Mining Accidents Using a Systematic Approach
Mostafa Mirzaei Aliabadi, Taleb Askaripoor, Hamed Aghaei
Journal of Occupational Hygiene Engineering.2021; 8(2): 8. CrossRef - Contributory factors interactions model: A new systems‐based accident model
Linlin Jing, Qingguo Bai, Weiqun Guo, Yan Feng, Lin Liu, Yingyu Zhang
Systems Research and Behavioral Science.2020; 37(2): 255. CrossRef - Game Modelling and Strategy Research on Trilateral Evolution for Coal-Mine Operational Safety Production System: A Simulation Approach
Yan Li, Yan Zhang, Haifeng Dai, Ziyan Zhao
Complexity.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - A Discourse on the Incorporation of Organizational Factors into Probabilistic Risk Assessment: Key Questions and Categorical Review
Justin Pence, Zahra Mohaghegh
Risk Analysis.2020; 40(6): 1183. CrossRef - Occupational Risks in the Extraction and Processing of Mineral Raw Materials
N V Gorlenko, M S Leonova, M A Murzin
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2020; 459(3): 032023. CrossRef - Structural equation modeling of risk-taking behaviors based on personality dimensions and risk power
MostafaMirzaei Aliabadi, Elnaz Taheri, Kamran Najafi, Farzaneh Mollabahrami, Sajjad Deyhim, Maryam Farhadian
International Archives of Health Sciences.2020; 7(3): 119. CrossRef - The Relationships Among Occupational Safety Climate, Patient Safety Climate, and Safety Performance Based on Structural Equation Modeling
Hamed Aghaei, Zahra Sadat Asadi, Mostafa Mirzaei Aliabadi, Hassan Ahmadinia
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2020; 53(6): 447. CrossRef - Analysis of the severity of occupational injuries in the mining industry using a Bayesian network
Mostafa Mirzaei Aliabadi, Hamed Aghaei, Omid kalatpuor, Ali Reza Soltanian, Asghar Nikravesh
Epidemiology and Health.2019; 41: e2019017. CrossRef - Cause Analysis of Unsafe Behaviors in Hazardous Chemical Accidents: Combined with HFACs and Bayesian Network
Xiaowei Li, Tiezhong Liu, Yongkui Liu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 17(1): 11. CrossRef

 KSE
KSE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite