Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Epidemiol Health > Volume 36; 2014 > Article
-
Methods
The clinical decision analysis using decision tree - Jong-Myon Bae
-
Epidemiol Health 2014;36:e2014025.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih/e2014025
Published online: October 30, 2014
Department of Preventive Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
- Correspondence: Jong-Myon Bae Department of Preventive Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, 102 Jejudaehak-ro, Jeju 690-756, Korea Tel: +82-64-755-5567, Fax: +82-64-725-2593, E-mail: jmbae@jejunu.ac.kr
• Received: September 9, 2014 • Accepted: October 29, 2014
©2014, Korean Society of Epidemiology
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- The clinical decision analysis (CDA) has used to overcome complexity and uncertainty in medical problems. The CDA is a tool allowing decision-makers to apply evidence-based medicine to make objective clinical decisions when faced with complex situations. The usefulness and limitation including six steps in conducting CDA were reviewed. The application of CDA results should be done under shared decision with patients’ value.
- Clinical practice, aimed at solving clinical problems of individual patients, is an act of continual decision-making. The best clinical decision refers to making a choice that maximizes effectiveness and minimizes harm [1]. Nevertheless, when the supporting evidences were scant, decision-making depends on the subjective intuition of the physician and then becomes unpredictable and non-reproducible [2].
- Around the 1990s, Evidence-based Medicine (EBM), which was suggested as a methodology for making clinical decisions based on the best evidence [3-6], expanded across the entire field of healthcare, and the terminology “evidence-based decision-making” was introduced [7-9]. By overcoming the complexity of medical environment [10-13] and the uncertainty of clinical decisions [14-17], the EBM aims to pursue qualitative improvements in healthcare [18-21]. Because clinical decisions are also directly related to the development and expansion of clinical treatment guidelines, approval of new drugs, drug prescriptions, the applicability of medical insurance for procedures, and healthcare policies [22,23].
- McCreery & Truelove [20] summarized five methodologies for decision-making: (1) Bayes’ theorem, (2) decision-tree design, (3) receiver-operating-characteristic curves, (4) sensitivity analysis, (5) utilities assessment. The clinical decision analysis (CDA) was suggested to make a clinical decision based on objectively quantitative indices calculated by using these methodologies [1]. This manuscript aims at reviewing the CDA methodology by definition, process, usefulness, and limitations.
INTRODUCTION
- Definition of clinical decision analysis
- In 1976, Bear & Schneiderman [24] suggested the terminology “clinical decision analysis” with the intention of applying the concept of decision analysis (DA), which had already been used in business and other social sciences, to the field of clinical practice. In order to understand the meaning of the term CDA, it is necessary to also look at the term DA coined by Raiffa [25] in 1968. In Appendix 1, paragraphs defining DA and CDA were arranged chronologically. CDA can be seen as a way of overcoming ‘uncertainty’ .
- Process of clinical decision analysis
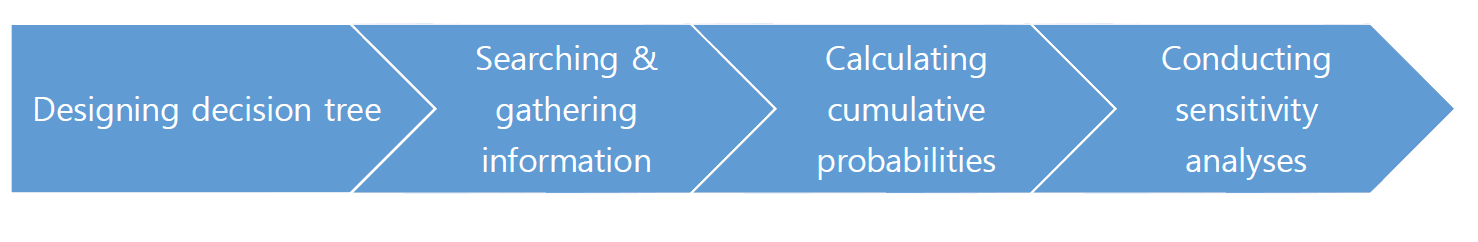
- Watts [26] proposed that CDA should consist of six stages including cost analysis, whereas Sackett et al. [27] proposed six stages including clinical practice. These process was well explained in the articles of Korah et al. [28] and Aleem et al. [1]. Depending on the methodology used, the CDA stages can be summarized as follows: (1) designing a decision tree showing all instances that can occur in a particular situation, (2) securing the likelihood and outcome utility values for each instance by conducting a literature search, (3) calculating the probabilities of cumulative expectation using the Bayesian theorem, and (4) performing a sensitivity analysis and assessing the variables needed for clinical decision-making (Figure 1).
- Since the content of the series of tasks that must be performed (including the construction of the decision tree) varies depending on the research questions [29], reference papers for different research questions are presented in Appendix 2. A detailed explanation is not included. Instead, the significance of performing a sensitivity analysis in the final stage will be discussed. The cumulative expectation probabilities obtained by using a decision tree vary according to the input values of outcome utility and likelihood [30]. Consequently, by estimating the vulnerability (how much the outcomes change according to fluctuations in the input values) the ultimate objective was to reduce uncertainty in decision-making [31]. In addition, sensitivity analysis could be used to elucidate the extent to which a given clinical situational variable affects the decision [28,32-34], so that these variables can be used as latent predictor variables for clinical prediction rules (CPR) [35-38]. Moreover, areas requiring future clinical research can be identified [39], and logical systematic errors in the designed decision tree can be debugged [30]. Traditional n-way sensitivity analysis [39,40] has been used as the statistical method for conducting a sensitivity analysis, but more recently, the Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulation methods [39,41-43] has been mainly used.
- In the CDA process, the most difficult stages are the design of the decision tree [1,40,44-46], the debugging of logical errors in the designed tree [30], the calculation of the cumulative probability, and the Monte Carlo simulation for the sensitivity analysis [47]. The recent development of the commercial software TreeAge Pro [48] is making these processes easier, and the importance of the literature search to find the appropriate values for analysis is being emphasized [1,49]. The latter is crucial since the meaning of the relevant values varies by country and generation [50,51].
- Usefulness of clinical decision analysis
- The usefulness of CDA in a clinical setting, being performed with the aim of overcoming complexity and uncertainty in clinical decisions, can be broadly summarized into three types.
- First, true to its original purpose, CDA provides the decision maker with objective evidence to make a judgment [1,52-55]. Consistent and reproducible decision-making can reduce the misuse of medical resources caused by uncertainty, improve the patient-physician relationship [18,30,56], and lead to qualitative improvements in healthcare [57,58].
- Second, CDA reveals the environmental variables that need to be considered when making a decision in a clinical setting [49,59,60]. This can be useful in decision-making not only for physicians, but also for medical insurance companies or decision-makers in healthcare administration [32,33,61].
- Third, by elucidating these predictor variables, the sensitivity analysis can be useful for CPR development, and can be applied to utility analysis and even cost analysis, as it reveals cases of insufficient evidence [5,26,33,60,62,63].
- Limitations of clinical decision analysis
- It has been claimed that the results obtained by CDA using a decision tree should only be used as a reference in decision-making, and are not guaranteed as absolute [45,64]. This implies that the CDA methodology has several limitations. Since CDA was proposed in 1970, doubts have been raised about its usefulness [57]. Aleem et al. [45] have presented a summary of these limitations from the perspective of a performance and of outcome analysis: (1) simplification errors may occur when measuring the final outcome of treatment decisions with indices such as quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) [1,32,49]; (2) performing a time-consuming analysis adequately in a busy clinical environment is difficult [45]; and (3) various factors (including potential harmful, expense, and patient preference for medical services) are involved in decision-making, and these cannot be accurately reflected in a decision tree [63,65]. Therefore, even if a CDA result is available, diverse decision-making is ultimately inevitable [10,66,67].
BODY
- Although the nature of medical treatment makes diverse decision-making inevitable, Black et al. [68] nevertheless emphasize the usefulness of CDA based on its ability to overcome uncertainty in medical treatment, and because the patient will encounter objective evidence through the internet or other sources as part of the shared decisions involving the patient. Considering the trends, four suggestions would be prepared to stimulate related research in South Korea:
- First, detailed care is required when interpreting the results of CDA studies and applying them to clinical practice. According to the standards for evaluating the validity and applicability of content from CDA papers [55,69-71], not only does an appropriate evaluation need to be performed, but the predicted likelihoods as the outcomes of the analysis must also be applied to a patient group rather than to individual patients [32]. In addition, data from persons of different nationalities used for CDA have different meanings [51]. In this regard, it is necessary to conduct related studies to gain data on Korean individuals. If CDA is performed, efforts to adhere to the seven principles demanded by Lurie & Sox [72] must be made.
- Second, the patients’ values must be reflected in decision-making. CDA relates to the combined value of the available evidences, but EBM [73-75] emphasizes that the manner in which this evidence is interpreted and reflected in the decision depends on the experiences of the clinical team [76] and the preferences of the patient [77]. In order to synthesize these three factors, Straus [78] proposed the likelihood of being helped or harmed index. In this way, shared decisions [79,80], meaning that decisions made together with the patient, are increasingly being demanded nowadays, and there is an emphasis on patient-centered clinical service [81,82]. This is in line with the principles of medical ethics [83-85] and can achieve the goal of restricting uncertainty in clinical treatment [14,86,87].
- Third, since the patient’s opinion should be positively reflected in the decision-making, decision aids for patients should be developed [88-90] in addition to increased CDA research. As seen in the various examples of decision aids described by O’Connor [91], decision aids are instruments that help making a value-based decision in accordance with the patient’s individual preferences but are different from educational material for patients [92]. Given that research has consistently shown that these instruments are helpful for patients [93-95], more decision aids for Korean patients must be developed.
- Fourth, CDA using decision trees, as dealt with in this manuscript, became active in the 1990s, and entering the 2000s various methodologies have been developed and are being applied to healthcare and medical treatment, such as supporting vector machines [96], random forest [97], and deep learning [98]. In the future, these methodologies must be investigated, so that they may be applied to various areas in healthcare with an understanding of their strengths and weaknesses.
CONCLUSION AND PROPOSALS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
- 1. Aleem IS, Schemitsch EH, Hanson BP. What is a clinical decision analysis study? Indian J Orthop 2008;42:137-139.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Banning M. A review of clinical decision making: models and current research. J Clin Nurs 2008;17:187-195.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Rosenberg WM, Sackett DL. On the need for evidence-based medicine. Therapie 1996;51:212-217.PubMed
- 4. Sackett DL. Evidence-based medicine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:1085-1086.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Djulbegovic B, Hozo I, Lyman GH. Linking evidence-based medicine therapeutic summary measures to clinical decision analysis. MedGenMed 2000;2:E6.
- 6. Bae JM, Park BJ, Ahn YO. Perspectives of clinical epidemiology in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc 2013;56:718-723 (Korean).Article
- 7. Dowie J. ‘Evidence-based’, ‘cost-effective’ and ‘preference-driven’ medicine: decision analysis based medical decision making is the pre-requisite. J Health Serv Res Policy 1996;1:104-113.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Teutsch SM, Berger ML. Evidence synthesis and evidence-based decision making: related but distinct processes. Med Decis Making 2005;25:487-489.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Bates DW, Kuperman GJ, Wang S, Gandhi T, Kittler A, Volk L, et al. Ten commandments for effective clinical decision support: making the practice of evidence-based medicine a reality. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2003;10:523-530.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Balla JI, Elstein AS, Christensen C. Obstacles to acceptance of clinical decision analysis. BMJ 1989;298:579-582.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Hamilton JD. Do we under utilise actuarial judgement and decision analysis? Evid Based Ment Health 2001;4:102-103.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Galanter CA, Patel VL. Medical decision making: a selective review for child psychiatrists and psychologists. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 2005;46:675-689.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Thompson C, Cullum N, McCaughan D, Sheldon T, Raynor P. Nurses, information use, and clinical decision making--the real world potential for evidence-based decisions in nursing. Evid Based Nurs 2004;7:68-72.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Beresford EB. Uncertainty and the shaping of medical decisions. Hastings Cent Rep 1991;21:6-11.Article
- 15. West AF, West RR. Clinical decision-making: coping with uncertainty. Postgrad Med J 2002;78:319-321.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Hu W, Kemp A, Kerridge I. Making clinical decisions when the stakes are high and the evidence unclear. BMJ 2004;329:852-854.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Thornton JG, Lilford RJ, Johnson N. Decision analysis in medicine. BMJ 1992;304:1099-1103.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Bae JM. Academic strategies based on evidence-practice gap. Hanyang Med Rev 2014;(in press).Article
- 19. Brazil K, Ozer E, Cloutier MM, Levine R, Stryer D. From theory to practice: improving the impact of health services research. BMC Health Serv Res 2005;5:1.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. McCreery AM, Truelove E. Decision making in dentistry. Part I: a historical and methodological overview. J Prosthet Dent 1991;65:447-451.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Myers J, McCabe SJ. Understanding medical decision making in hand surgery. Clin Plast Surg 2005;32:453-461.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Atkins D. Creating and synthesizing evidence with decision makers in mind: integrating evidence from clinical trials and other study designs. Med Care 2007;45:S16-S22.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Garrison LP Jr, Neumann PJ, Erickson P, Marshall D, Mullins CD. Using real-world data for coverage and payment decisions: the ISPOR Real-World Data Task Force report. Value Health 2007;10:326-335.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Bear R, Schneiderman J. Decision analysis in clinical medicine. Can Med Assoc J 1976;115:833-836.PubMedPMC
- 25. Raiffa H. Decision analysis; introductory lectures on choices under uncertainty. MD Comput 1993;10:312-328.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Watts NT. Clinical decision analysis. Phys Ther 1989;69:569-576.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Sackett DL, Haynes RB, Guyatt GH, Tugwell P. Clinical epidemiology: a basic science for clinical medicine. 2nd. Boston: Little, Brown; 1991. p 140-145.
- 28. Korah S, Thomas R, Muliyil J. An introduction to clinical decision analysis in ophthalmology. Indian J Ophthalmol 1999;47:41-48.PubMed
- 29. Lilford RJ, Pauker SG, Braunholtz DA, Chard J. Decision analysis and the implementation of research findings. BMJ 1998;317:405-409.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Krahn MD, Naglie G, Naimark D, Redelmeier DA, Detsky AS. Primer on medical decision analysis: part 4--analyzing the model and interpreting the results. Med Decis Making 1997;17:142-151.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Briggs AH. Handling uncertainty in cost-effectiveness models. Pharmacoeconomics 2000;17:479-500.ArticlePubMed
- 32. van der Velde G. Clinical decision analysis: an alternate, rigorous approach to making clinical decisions and developing treatment recommendations. J Can Chiropr Assoc 2005;49:258-263.PubMedPMC
- 33. Graham B, Detsky AS. The application of decision analysis to the surgical treatment of early osteoarthritis of the wrist. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2001;83:650-654.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Hirai S, Ono J, Odaki M, Serizawa T, Sato M, Isobe K, et al. Treatment of asymptomatic unruptured intracranial aneurysms. A clinical decision analysis. Interv Neuroradiol 2001;7:61-64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Huijbregts P. Clinical prediction rules: time to sacrifice the holy cow of specificity? J Man Manip Ther 2007;15:5-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Cook CE. Potential pitfalls of clinical prediction rules. J Man Manip Ther 2008;16:69-71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Ingui BJ, Rogers MA. Searching for clinical prediction rules in MEDLINE. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2001;8:391-397.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Vickers AJ, Cronin AM. Traditional statistical methods for evaluating prediction models are uninformative as to clinical value: towards a decision analytic framework. Semin Oncol 2010;37:31-38.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Aoki N, Beck JR, Kitahara T, Ohbu S, Soma K, Ohwada T, et al. Reanalysis of unruptured intracranial aneurysm management: effect of a new international study on the threshold probabilities. Med Decis Making 2001;21:87-96.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Hagen MD. Decision analysis: a review. Fam Med 1992;24:349-354.PubMed
- 41. Minelli C, Abrams KR, Sutton AJ, Cooper NJ. Benefits and harms associated with hormone replacement therapy: clinical decision analysis. BMJ 2004;328:371.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Naimark D, Krahn MD, Naglie G, Redelmeier DA, Detsky AS. Primer on medical decision analysis: part 5--Working with Markov processes. Med Decis Making 1997;17:152-159.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Doubilet P, Begg CB, Weinstein MC, Braun P, McNeil BJ. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis using Monte Carlo simulation. A practical approach. Med Decis Making 1985;5:157-177.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Podgorelec V, Kokol P, Stiglic B, Rozman I. Decision trees: an overview and their use in medicine. J Med Syst 2002;26:445-463.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Aleem IS, Jalal H, Aleem IS, Sheikh AA, Bhandari M. Clinical decision analysis: incorporating the evidence with patient preferences. Patient Prefer Adherence 2009;3:21-24.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. Detsky AS, Naglie G, Krahn MD, Redelmeier DA, Naimark D. Primer on medical decision analysis: part 2--building a tree. Med Decis Making 1997;17:126-135.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Doan A, Haddawy P, Kahn CE Jr. Decision-theoretic refinement planning: a new method for clinical decision analysis. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care 1995;299-303.PubMedPMC
- 48. TreeAge Software Inc. TreeAge pro healthcare. [cited 2014 Sep 9]. Available from: https://www.treeage.com/shop/treeage-pro-healthcare/ .
- 49. Naglie G, Krahn MD, Naimark D, Redelmeier DA, Detsky AS. Primer on medical decision analysis: part 3--Estimating probabilities and utilities. Med Decis Making 1997;17:136-141.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Torrance GW. Utility approach to measuring health-related quality of life. J Chronic Dis 1987;40:593-603.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Clancy CM, Cronin K. Evidence-based decision making: global evidence, local decisions. Health Aff (Millwood) 2005;24:151-162.ArticlePubMed
- 52. Sarasin FP. Decision analysis and its application in clinical medicine. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;94:172-179.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Yentis SM. Decision analysis in anaesthesia: a tool for developing and analysing clinical management plans. Anaesthesia 2006;61:651-658.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Sisson JC, Schoomaker EB, Ross JC. Clinical decision analysis. The hazard of using additional data. JAMA 1976;236:1259-1263.ArticlePubMed
- 55. Richardson WS, Detsky AS. Users’ guides to the medical literature. VII. How to use a clinical decision analysis. A. Are the results of the study valid? Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA 1995;273:1292-1295.ArticlePubMed
- 56. Kassirer JP, Moskowitz AJ, Lau J, Pauker SG. Decision analysis: a progress report. Ann Intern Med 1987;106:275-291.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Dolan JG. Clinical decision analysis. Med Decis Making 2001;21:150-151.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Pauker SG, Kassirer JP. Decision analysis. N Engl J Med 1987;316:250-258.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Stockstill JW, Bowley JF, Attanasio R. Clinical decision analysis in fixed prosthodontics. Dent Clin North Am 1992;36:569-580.ArticlePubMed
- 60. McCreery AM, Truelove E. Decision making in dentistry. Part II: clinical applications of decision methods. J Prosthet Dent 1991;65:575-585.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Burd RS, Sonnenberg FA. Decision analysis: a basic overview for the pediatric surgeon. Semin Pediatr Surg 2002;11:46-54.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Burford B, Lewin S, Welch V, Rehfuess E, Waters E. Assessing the applicability of findings in systematic reviews of complex interventions can enhance the utility of reviews for decision making. J Clin Epidemiol 2013;66:1251-1261.ArticlePubMed
- 63. Burch J, Hinde S, Palmer S, Beyer F, Minton J, Marson A, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of technologies used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery: a systematic review and decision-analytical model. Health Technol Assess 2012;16:1-157.Article
- 64. Buchanan JG. An introduction to clinical decision analysis: bone marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia. Aust N Z J Med 1983;13:451-456.ArticlePubMed
- 65. Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, Swiontkowski MF, Tornetta P 3rd, Obremskey W, Koval KJ, et al. Internal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A:1673-1681.ArticlePubMed
- 66. Brookhart MA, Solomon DH, Wang P, Glynn RJ, Avorn J, Schneeweiss S. Explained variation in a model of therapeutic decision making is partitioned across patient, physician, and clinic factors. J Clin Epidemiol 2006;59:18-25.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Sekimoto M, Imanaka Y, Kitano N, Ishizaki T, Takahashi O. Why are physicians not persuaded by scientific evidence? A grounded theory interview study. BMC Health Serv Res 2006;6:92.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Blank T, Graves K, Sepucha K, Llewellyn-Thomas H. Understanding treatment decision making: contexts, commonalities, complexities, and challenges. Ann Behav Med 2006;32:211-217.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Brocklehurst P, Roberts T. Should acyclovir prophylaxis be used in late pregnancy in women with recurrent genital herpes infection? How to use a clinical decision analysis. Genitourin Med 1997;73:314-319.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Richardson WS, Detsky AS. Users’ guides to the medical literature. VII. How to use a clinical decision analysis. B. What are the results and will they help me in caring for my patients? Evidence Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA 1995;273:1610-1613.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Thornhill J, Judd M, Clements D. CHSRF knowledge transfer: (re)introducing the self-assessment tool that is helping decision-makers assess their organization’s capacity to use research. Healthc Q 2009;12:22-24.Article
- 72. Lurie JD, Sox HC. Principles of medical decision-making. Spine 1999;24:493-498.ArticlePubMed
- 73. Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JA, Haynes RB, Richardson WS. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t. BMJ 1996;312:71-72.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 74. Barratt A. Evidence Based Medicine and Shared Decision-making: the challenge of getting both evidence and preferences into health care. Patient Educ Couns 2008;73:407-412.ArticlePubMed
- 75. Tilburt JC. Evidence-based medicine beyond the bedside: keeping an eye on context. J Eval Clin Pract 2008;14:721-725.ArticlePubMed
- 76. Dans AL, Dans LF, Guyatt GH, Richardson S. Users’ guides to the medical literature: XIV. How to decide on the applicability of clinical trial results to your patient. Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA 1998;279:545-549.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Goetghebeur MM, Wagner M, Khoury H, Levitt RJ, Erickson LJ, Rindress D. Evidence and Value: impact on DEcisionMaking--the EVIDEM framework and potential applications. BMC Health Serv Res 2008;8:270.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 78. Straus SE. Individualizing treatment decisions. The likelihood of being helped or harmed. Eval Health Prof 2002;25:210-224.ArticlePubMed
- 79. Godolphin W. Shared decision-making. Healthc Q 2009;12 Spec No Patient:e186-e190.Article
- 80. Bate L, Hutchinson A, Underhill J, Maskrey N. How clinical decisions are made. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2012;74:614-620.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Barry MJ, Edgman-Levitan S. Shared decision-making--pinnacle of patient-centered care. N Engl J Med 2012;366:780-781.ArticlePubMed
- 82. Oshima Lee E, Emanuel EJ. Shared decision-making to improve care and reduce costs. N Engl J Med 2013;368:6-8.ArticlePubMed
- 83. ter Meulen RH. The ethical basis of the precautionary principle in health care decision-making. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005;207:663-667.ArticlePubMed
- 84. Tannahill A. Beyond evidence--to ethics: a decision-making framework for health promotion, public health and health improvement. Health Promot Int 2008;23:380-390.ArticlePubMed
- 85. Berger JT, DeRenzo EG, Schwartz J. Surrogate decision-making: reconciling ethical theory and clinical practice. Ann Intern Med 2008;149:48-53.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Kass NE. Early phase clinical trials: communicating the uncertainties of ‘magnitude of benefit’ and ‘likelihood of benefit’. Clin Trials 2008;5:627-629.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 87. Légaré F, Brouillette MH. Shared decision-making in the context of menopausal health: where do we stand? Maturitas 2009;63:169-175.ArticlePubMed
- 88. Légaré F, Moher D, Elwyn G, LeBlanc A, Gravel K. Instruments to assess the perception of physicians in the decision-making process of specific clinical encounters: a systematic review. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2007;7:30.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 89. Stacey D, Samant R, Bennett C. Decision-making in oncology: a review of patient decision aids to support patient participation. CA Cancer J Clin 2008;58:293-304.ArticlePubMed
- 90. Elwyn G, Stiel M, Durand MA, Boivin J. The design of patient decision support interventions: addressing the theory-practice gap. J Eval Clin Pract 2011;17:565-574.ArticlePubMed
- 91. O’Connor A. Using patient decision aids to promote evidence-based decision-making. ACP J Club 2001;135:A11-A12.Article
- 92. O’Connor AM. Using decision aids to help patients navigate the “grey zone” of medical decision-making. CMAJ 2007;176:1597-1598.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 93. Roshanov PS, Fernandes N, Wilczynski JM, Hemens BJ, You JJ, Handler SM, et al. Features of effective computerised clinical decision support systems: meta-regression of 162 randomised trials. BMJ 2013;346:f657.ArticlePubMed
- 94. O’Connor AM, Bennett C, Stacey D, Barry MJ, Col NF, Eden KB, et al. Do patient decision aids meet effectiveness criteria of the international patient decision aid standards collaboration? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Decis Making 2007;27:554-574.ArticlePubMed
- 95. Liu J, Wyatt JC, Altman DG. Decision tools in health care: focus on the problem, not the solution. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2006;6:4.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 96. Chen T, Wang Y, Chen H, Marder K, Zeng D. Targeted local support vector machine for age-dependent classification. J Am Stat Assoc 2014;109:1174-1187.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 97. Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn 2001;45:5-32.Article
- 98. Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh YW. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput 2006;18:1527-1554.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Appendix
Appendix 1.
| Sources references | Related sentences | |
|---|---|---|
| DA | A01 | DA -an explicit, normative and analytic approach to making decisions under uncertainty- provides a probabilistic framework for exploring difficult problems in non-deterministic domains. |
| A02 | DA is the application of explicit, quantitative methods to analyze decisions under conditions of uncertainty. | |
| A03 | DA formalizes the decision process, highlights the factors that influence the decision, and applies mathematical rigour to quantify decision-making. | |
| CDA | A04 | CDA seeks to identify the optimal management strategy by modelling the uncertainty and risks entailed in the diagnosis, natural history, and treatment of a particular problem or disorder. |
| A05 | CDA is a systematic method for making wise choices under just such circumstances. | |
| A06 | (C)DA in a quantitative approach for dealing with the uncertainties inherent in many medical decisions, including decisions about genetic testing. | |
| A07 | (C)DA is a quantitative by an ever increasing number of costly and confusing application of probability and utility theory to decision diagnostic tests and therapeutic interventions, decision-making under conditions of uncertainty. | |
| A08 | (C)DA is a quantitative approach to decision-making under conditions of uncertainty that can be applied to specific types of clinical problems. | |
| A09 | CDA is a process whereby different treatment options are assessed systematically. | |
| A10 | (C)DA is a formal, mathematical approach to analyzing difficult decisions faced by clinical decision makers (i.e. patients, clinicians, policy-makers). | |
| A11 | (C)DA is a formal, quantitative method for systematically comparing the benefits and harms of alternative clinical strategies under circumstances of uncertainty. | |
| A12 | (C)DA is a tool that allows users to apply evidence-based medicine to make informed and objective clinical decisions when faced with complex situations. | |
| A13 | (C)DA is a simulation, model-based research technique in which investigators combine information from a variety of sources to create a mathematical model representing a clinical decision. | |
| A14 | CDA - the application of DA to a clinical or patient-based setting - is a technique that incorporates literature-derived probabilities with expert and patient preferences to result in an informed clinical decision. |
- A01. Wong JB, Moskowitz AJ, Pauker SG. Clinical decision analysis using microcomputers. A case of coexistent hepatocellular carcinoma and abdominal aortic aneurysm. West J Med 1986;145:805-815.PubMedPMC
- A02. Richardson WS, Detsky AS. Users' guides to the medical literature. VII. How to use a clinical decision analysis. A. Are the results of the study valid? Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA 1995;273:1292-1295.Article
- A03. Sonnenberg A. Patient-physician discordance about benefits and risks in gastroenterology decision-making. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;19:1247-1253.ArticlePubMed
- A04. Doan A, Haddawy P, Kahn CE Jr. Decision-theoretic refinement planning: a new method for clinical decision analysis. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care 1995;299-303.PubMedPMC
- A05. Watts NT. Clinical decision analysis. Phys Ther 1989;69:569-576.ArticlePubMed
- A06. McConnell LM, Goldstein MK. The application of medical decision analysis to genetic testing: an introduction. Genet Test 1999;3:65-70.ArticlePubMed
- A07. Sarasin FP. Decision analysis and its application in clinical medicine. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;94:172-179.ArticlePubMed
- A08. Burd RS, Sonnenberg FA. Decision analysis: a basic overview for the pediatric surgeon. Semin Pediatr Surg 2002;11:46-54.ArticlePubMed
- A09. Manarey CR, Westerberg BD, Marion SA. Clinical decision analysis in the treatment of acute otitis media in a child over 2 years of age. J Otolaryngol 2002;31:23-30.ArticlePubMed
- A10. van der Velde G. Clinical decision analysis: an alternate, rigorous approach to making clinical decisions and developing treatment recommendations. J Can Chiropr Assoc 2005;49:258-263.PubMedPMC
- A11. Elkin EB, Vickers AJ, Kattan MW. Primer: using decision analysis to improve clinical decision-making in urology. Nat Clin Pract Urol 2006;3:439-448.ArticlePubMed
- A12. Aleem IS, Schemitsch EH, Hanson BP. What is a clinical decision analysis study? Indian J Orthop 2008;42:137-139.ArticlePubMedPMC
- A13. O’Brien SH. Decision analysis in pediatric hematology. Pediatr Clin North Am 2008;55:287-304.ArticlePubMed
- A14. Aleem IS, Jalal H, Aleem IS, Sheikh AA, Bhandari M. Clinical decision analysis: incorporating the evidence with patient preferences. Patient Prefer Adherence 2009;3:21-24.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B01. Pauker SG, Kassirer JP. The threshold approach to clinical decision-making. N Engl J Med 1980;302:1109-1117.Article
- B02. Harber P, Rappaport S. Clinical decision analysis in occupational medicine. Choosing the optimal FEV1 criterion for diagnosing occupational asthma. J Occup Med 1985;27:651-658.PubMed
- B03. Gando S, Nanzaki S, Kemmotsu O. Disseminated intravascular coagulation and sustained systemic inflammatory response syndrome predict organ dysfunctions after trauma: application of clinical decision analysis. Ann Surg 1999;229:121-127.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B04. Connock M, Frew E, Evans BW, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review. Health Technol Assess 2006;10:1-118.Article
- B05. Pauker SP, Pauker SG. Prenatal diagnosis: a directive approach to genetic counseling using decision analysis. Yale J Biol Med 1977;50:275-289.PubMedPMC
- B06. Krahn MD, Mahoney JE, Eckman MH, Trachtenberg J, Pauker SG, Detsky AS. Screening for prostate cancer. A decision analytic view. JAMA 1994;272:773-780.Article
- B07. Mol BW, Verhagen TE, Hendriks DJ, Collins JA, Coomarasamy A, Opmeer BC, et al. Value of ovarian reserve testing before IVF: a clinical decision analysis. Hum Reprod 2006;21:1816-1823.ArticlePubMed
- B08. Burch J, Hinde S, Palmer S, Beyer F, Minton J, Marson A, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of technologies used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery: a systematic review and decision-analytical model. Health Technol Assess 2012;16:1-157.Article
- B09. Johnson N, Lilford RJ, Jones SE, McKenzie L, Billingsley P, Songane FF. Using decision analysis to calculate the optimum treatment for microinvasive cervical cancer. Br J Cancer 1992;65:717-722.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B10. Gariepy AM, Creinin MD, Schwarz EB, Smith KJ. Reliability of laparoscopic compared with hysteroscopic sterilization at 1 year: a decision analysis. Obstet Gynecol 2011;118:273-279.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B11. Aoki N, Beck JR, Kitahara T, Ohbu S, Soma K, Ohwada T, et al. Reanalysis of unruptured intracranial aneurysm management: effect of a new international study on the threshold probabilities. Med Decis Making 2001;21:87-96.ArticlePubMed
- B12. Liu D, Lehmann HP, Frick KD, Carter HB. Active surveillance versus surgery for low risk prostate cancer: a clinical decision analysis. J Urol 2012;187:1241-1246.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B13. Willis SR, Ahmed HU, Moore CM, Donaldson I, Emberton M, Miners AH, et al. Multiparametric MRI followed by targeted prostate biopsy for men with suspected prostate cancer: a clinical decision analysis. BMJ Open 2014;4:e004895.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B14. Minelli C, Abrams KR, Sutton AJ, Cooper NJ. Benefits and harms associated with hormone replacement therapy: clinical decision analysis. BMJ 2004;328:371.ArticlePubMedPMC
- B15. Perreault S, Levinton C, Laurier C, Moride Y, Ste-Marie LG, Crott R. Validation of a decision model for preventive pharmacological strategies in postmenopausal women. Eur J Epidemiol 2005;20:89-101.ArticlePubMed
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Advancements in medical diagnosis and treatment through machine learning: A review
Mohammad Ahsan, Anam Khan, Kaif Rehman Khan, Bam Bahadur Sinha, Anamika Sharma
Expert Systems.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive model for identifying mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A CHAID decision tree analysis
Rehanguli Maimaitituerxun, Wenhang Chen, Jingsha Xiang, Yu Xie, Fang Xiao, Xin Yin Wu, Letao Chen, Jianzhou Yang, Aizhong Liu, Wenjie Dai
Brain and Behavior.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of spinal trauma care and outcomes in a resource-constrained environment: a decision tree analysis of spinal trauma surgery and outcomes in Tanzania
Andreas Leidinger, Scott L. Zuckerman, Yueqi Feng, Yitian He, Xinrui Chen, Beverly Cheserem, Linda M. Gerber, Noah L. Lessing, Hamisi K. Shabani, Roger Härtl, Halinder S. Mangat
Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Teaching the science of uncertainty
Glenn Moulder, Emily Harris, Lekshmi Santhosh
Diagnosis.2023; 10(1): 13. CrossRef - Comparison of decision tree with common machine learning models for prediction of biguanide and sulfonylurea poisoning in the United States: an analysis of the National Poison Data System
Omid Mehrpour, Farhad Saeedi, Samaneh Nakhaee, Farbod Tavakkoli Khomeini, Ali Hadianfar, Alireza Amirabadizadeh, Christopher Hoyte
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Wearable Sensors and Multilevel Gait Assessment: A Machine Learning Ensemble Approach
Younghoon Jeon, Jaeyong Kang, Byeong C. Kim, Kun Ho Lee, Jong-In Song, Jeonghwan Gwak
IEEE Sensors Journal.2023; 23(9): 10041. CrossRef - A Clinical Decision Tree to Support Keratoconus Patients Considering Corneal Cross-Linking Combined with Refractive Treatment
Katja Iselin, Lucas Bachmann, Philipp Baenninger, Frantisek Sanak, Claude Kaufmann
Klinische Monatsblätter für Augenheilkunde.2023; 240(04): 379. CrossRef - Reverse Engineering of Maintenance Budget Allocation Using Decision Tree Analysis for Data-Driven Highway Network Management
Azam Amir, Michael Henry
Sustainability.2023; 15(13): 10467. CrossRef - Case studies of clinical decision-making through prescriptive models based on machine learning
William Hoyos, Jose Aguilar, Mayra Raciny, Mauricio Toro
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2023; 242: 107829. CrossRef - Assessment of a venous thromboembolism prophylaxis shared decision-making intervention (DASH-TOP) using the decisional conflict scale: a mixed-method study
Montserrat León‑García, Brittany Humphries, Pablo Roca Morales, Derek Gravholt, Mark H. Eckman, Shannon M. Bates, Nataly R. Espinoza Suárez, Feng Xie, Lilisbeth Perestelo‑Pérez, Pablo Alonso‑Coello
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Open-Access Dataset of Hospitalized Cardiac-Arrest Patients: Machine-Learning-Based Predictions Using Clinical Documentation
Lahiru Theekshana Weerasinghe Rajapaksha, Sugandima Mihirani Vidanagamachchi, Sampath Gunawardena, Vajira Thambawita
BioMedInformatics.2023; 4(1): 34. CrossRef - Economic evaluation of Zika Contraception Access Network in Puerto Rico during the 2016–17 Zika virus outbreak
Rui Li, Sascha R. Ellington, Romeo R. Galang, Scott D. Grosse, Zipatly Mendoza, Stacey Hurst, Yari Vale, Eva Lathrop, Lisa Romero
Contraception.2022; 107: 68. CrossRef - Cognitive Status Predicts Return to Functional Independence After Minor Stroke: A Decision Tree Analysis
Mirjam R. Heldner, Caroline Chalfine, Marion Houot, Roza M. Umarova, Jan Rosner, Julian Lippert, Laura Gallucci, Anne Leger, Flore Baronnet, Yves Samson, Charlotte Rosso
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A machine-learning-based prediction method for easy COPD classification based on pulse oximetry clinical use
Claudia Abineza, Valentina E. Balas, Philibert Nsengiyumva, Valentina Emilia Balas
Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems.2022; 43(2): 1683. CrossRef -
Liquid biopsies for early diagnosis of brain tumours:
in
silico
mathematical biomarker modelling
Johanna A. Blee, Xia Liu, Abigail J. Harland, Kavi Fatania, Stuart Currie, Kathreena M. Kurian, Sabine Hauert
Journal of The Royal Society Interface.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Chatbot for Pregnant Women on a Posyandu Application in Indonesia: From Qualitative Approach to Decision Tree Method
Indriana Widya Puspitasari, Fedri Ruluwedrata Rinawan, Wanda Gusdya Purnama, Hadi Susiarno, Ari Indra Susanti
Informatics.2022; 9(4): 88. CrossRef - Data mining techniques on astronomical spectra data – II. Classification analysis
Haifeng Yang, Lichan Zhou, Jianghui Cai, Chenhui Shi, Yuqing Yang, Xujun Zhao, Juncheng Duan, Xiaona Yin
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.2022; 518(4): 5904. CrossRef - Towards a new understanding of uncertainty in medical education
Ciara Lee, Katherine Hall, Megan Anakin, Ralph Pinnock
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice.2021; 27(5): 1194. CrossRef - Estimating assistive product need in Cameroon and India: results of population‐based surveys and comparison of self‐report and clinical impairment assessment approaches
Dorothy Boggs, Hannah Kuper, Islay Mactaggart, GVS Murthy, Joseph Oye, Sarah Polack
Tropical Medicine & International Health.2021; 26(2): 146. CrossRef - Decision tree modeling in R software to aid clinical decision making
Elena G. Toth, David Gibbs, Jackie Moczygemba, Alexander McLeod
Health and Technology.2021; 11(3): 535. CrossRef - Non-Linear Algorithms in Supervised Classical Machine Learning
Monalisa Patel, John B. Tan, Fu-Sheng Chou
Neonatology Today.2021; 16(7): 40. CrossRef - MEDICARE AI-ASSISTED AI IN HEALTHCARE
Nitish Nagar, Plaban Roy, Saurabh Deswal, Parth Pandya, Aashna Bhardwaj, Parisa Naraei
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 40. CrossRef - Dose Adjustment Model of Paliperidone in Patients With Acute Schizophrenia: A post hoc Analysis of an Open-Label, Single-Arm Multicenter Study
Tianmei Si, Ling Sun, Yilong Zhang, Lili Zhang
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Opportunities and Challenges for Machine Learning in Rare Diseases
Sergio Decherchi, Elena Pedrini, Marina Mordenti, Andrea Cavalli, Luca Sangiorgi
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Toma de decisiones en pacientes psiquiátricos: un estudio cualitativo con grupos focales
Ricardo de la Espriella
Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatría.2020; 49(4): 231. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence with multi-functional machine learning platform development for better healthcare and precision medicine
Zeeshan Ahmed, Khalid Mohamed, Saman Zeeshan, XinQi Dong
Database.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel and simple machine learning algorithm for preoperative diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children
Emrah Aydin, İnan Utku Türkmen, Gözde Namli, Çiğdem Öztürk, Ayşe B. Esen, Y. Nur Eray, Egemen Eroğlu, Fatih Akova
Pediatric Surgery International.2020; 36(6): 735. CrossRef - Use of Decision Analysis and Economic Evaluation in Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review
Gabriel Bouhadana, Tyler Safran, Becher Al-Halabi, Peter G. Davison
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open.2020; 8(4): e2786. CrossRef - Applying Machine Learning for Healthcare: A Case Study on Cervical Pain Assessment with Motion Capture
Juan de la Torre, Javier Marin, Sergio Ilarri, Jose J. Marin
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(17): 5942. CrossRef - Clinical Solutions: Factors and Problematic Situations from the Perspective of Doctors in a Large Russian City
Anna S. Gotlib, Vitaly L. Lekhtsier
Sociological Journal.2020; 26(3): 114. CrossRef - Shared Decision Making in Endodontics
Sandhya Rajagopal, Aengus Kelly
Primary Dental Journal.2020; 9(4): 31. CrossRef - Decision making in psychiatric patients: A qualitative study with focus groups
Ricardo de la Espriella
Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatría (English ed.).2020; 49(4): 231. CrossRef - Diagnostic Precision in Neonatal Medicine: Why Over Investigate?
Adil Khan, Shabih Manzar
Neonatology Today.2020; 15(8): 15. CrossRef - Morphometric MRI profiles of multiple system atrophy variants and implications for differential diagnosis
Florian Krismer, Klaus Seppi, Georg Göbel, Ruth Steiger, Isabel Zucal, Sylvia Boesch, Elke R. Gizewski, Gregor K. Wenning, Werner Poewe, Christoph Scherfler
Movement Disorders.2019; 34(7): 1041. CrossRef - Use of Decision Analysis and Economic Evaluation in Upper Extremity Surgery: A Systematic Review
Tyler Safran, Helene Retrouvey, Kevin Gorsky, Heather L. Baltzer
Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery.2019; 144(2): 395. CrossRef - Assessing the Impact of Ozone and Particulate Matter on Mortality Rate from Respiratory Disease in Seoul, Korea
Park
Atmosphere.2019; 10(11): 685. CrossRef - Systematic scoping review protocol for clinical prediction rules (CPRs) in the management of patients with spinal cord injuries
Blake Boggenpoel, Vuyolwethu Madasa, Tarryn Jeftha, Conran Joseph
BMJ Open.2019; 9(1): e025076. CrossRef - Risk factors of psychiatric hospitalization of military service persons in Taiwan: Preliminary results from unsupervised clustering techniques
Geng-Fu Tsai, Yueh-Ming Tai, Sy-Ming Guu
Taiwanese Journal of Psychiatry.2019; 33(2): 105. CrossRef - Thrombectomy of Ventricular Assist Device‐Originated Embolic Stroke: A Clinical Decision Model
Kalea L. Colletta, Barak Bar, Max J. Liebo, Ewa Borys, Michael J. Schneck, Camilo R. Gomez
Journal of Neuroimaging.2019; 29(4): 423. CrossRef - An ethical evaluation index system for clinical approval of medical technology in China: A structural equation model study
Jing-xian Li, Zhi-cheng Qiao, Hong-xia Ma, Yi-ting Li, En-chang Li, Peng-cheng Ji, Gang Huang
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 23(6): 474. CrossRef - Letter: NICE referral criteria for lower gastrointestinal alarm features – not ideal but not poor either
L. Min, Y. Zhao, J. Xing, S. Zhang
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2017; 45(8): 1175. CrossRef - The value of decision tree analysis in planning anaesthetic care in obstetrics
J.H. Bamber, S.A. Evans
International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia.2016; 27: 55. CrossRef - Value-based medicine: concepts and application
Jong-Myon Bae
Epidemiology and Health.2015; 37: e2015014. CrossRef - Development and application of patient decision aids
Jong-Myon Bae
Epidemiology and Health.2015; 37: e2015018. CrossRef

 KSE
KSE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite


